
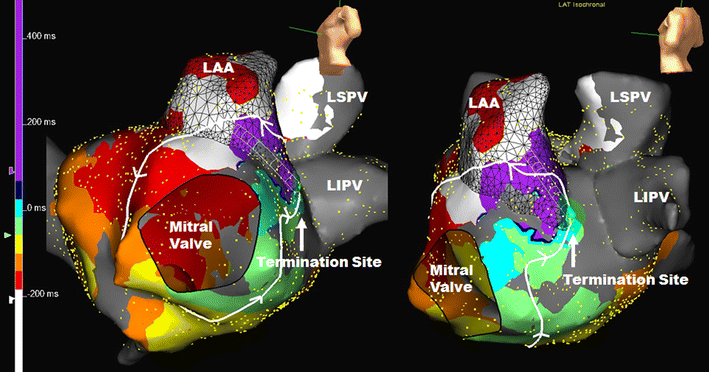
Advanced Renal dysfunction (eGFR<30 ml/min) Indwelling cardiac resynchronisation therapy device, pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator Implanted metal prosthetic valve(s) in mitral position Extreme frailty (A score of 7,8 or worse on the Clinical Frailty Scale) Inability or unwillingness to take oral anticoagulant treatment Recent stroke/transient ischaemic attack within 3 months Severe left ventricular dysfunction (LV ejection fraction < 30% on Echocardiography) Left atrial diameter (PLAX M-mode) >5.5 cm Indwelling atrial-septal defect occluder device, or any anatomical reason that precludes left atrial access History of atrial flutter with 1:1 atrioventricular conduction and haemodynamic compromise Atrial flutter morphology on ECG suggestive of a left atrial flutter Atrial flutter documented solely on Ambulatory monitoring Previous cavo-tricuspid isthmus ablation or atrial fibrillation ablation Any evidence of previously documented atrial fibrillation In the view of the treating physician, the ECG morphology should be compatible with a CTI-dependent circuit, either counterclockwise or clockwise. The atrial flutter may be either persistent or paroxysmal, with at least one episode having been documented on 12-lead ECG. Patients referred for catheter ablation for typical atrial flutter. This study aims to demonstrate that standalone cryoballoon PVI for typical atrial flutter without RF CTI ablation will lead to a significant difference in preventing recurrence of atrial arrhythmia compared to radiofrequency ablation of the CTI, and should be offered as first-line therapy. In patients with both atrial flutter and fibrillation, PVI alone has been shown to control both types of atrial arrhythmia, with no benefit derived from supplemental RF CTI ablation.
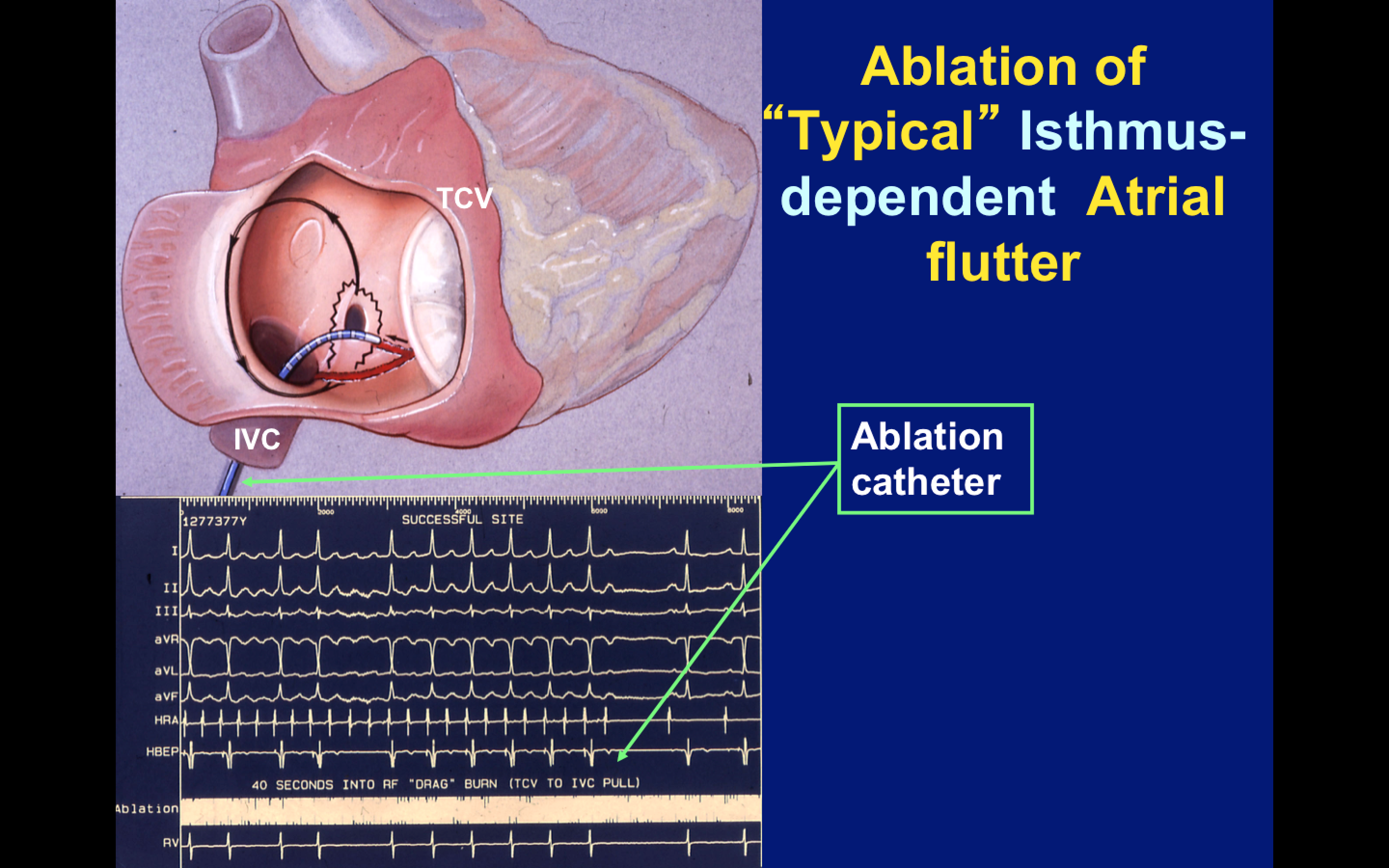
Radiofrequency (RF) ablation of the cavo-tricuspid isthmus (CTI) is the current accepted first-line treatment for atrial flutter, although post-ablation atrial fibrillation commonly occurs, even in the absence of pre-existing atrial fibrillation.Ĭryoballoon Pulmonary Vein Isolation (PVI) has become an established treatment for atrial fibrillation. Cavo-tricuspid isthmus-dependent atrial flutter almost always results from short bursts of antecedent atrial fibrillation. Why Should I Register and Submit Results?Ītrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are believed to share the same initiating triggers in the form of pulmonary vein ectopy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
